Labeled Antibodies
Labels for detecting antibodies
Antibodies are labeled with various substances for detection. When using a commercial kit to label antibodies, care must be taken not to lose the activity of the antibody.
Common types of labels
- Fluorescent labelling
- Enzyme labelling
- Biotin
- Magnetic beads, agarose beads, magnetic agarose beads
- Colloidal gold
Fluorescent labelling
Fluorescent labeled antibodies are used for flow cytometry and immunofluorescence staining. Multpile antibodies with different fluorescent labels can be used for double or triple staining.
Common fluorphores
| Types of Fluorophore | |
|---|---|
| Fluorescent dye (Low molecular weight fluorescent dye) |
FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate), Alexa Fluor®, Cy dyes, etc. |
| Fluorescent protein | PE (phycoerythrin), APC (allophycocyanin), etc |
Application example of fluorescent-labeled antibody: Immunofluorescence staining
Immunofluorescence staining with an antibody to an organelle marker.
HeLa cells were stained with an antibody to the Golgi protein GM130.
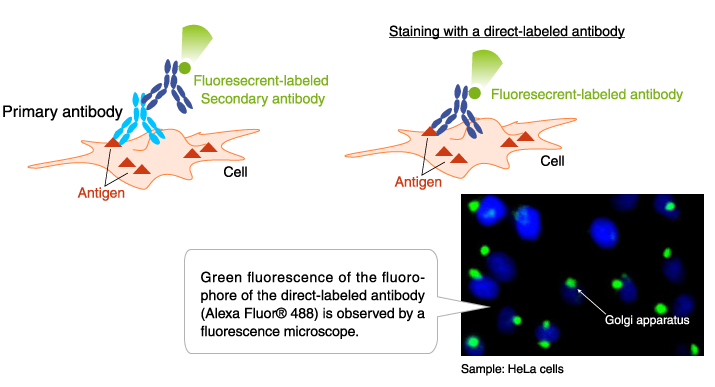
Direct-labeled antibody: Anti-GM130 mAb-Alexa Fluor® 488 (Code No. M179-A48)
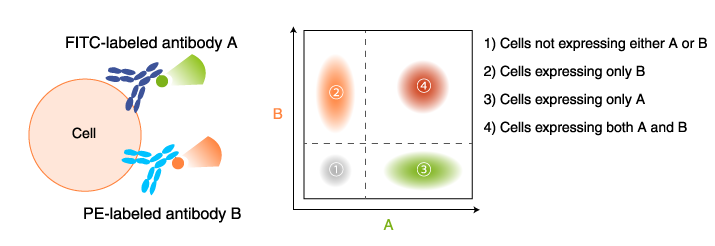
Application example of fluorescent-labeled antibody: Flow cytometry
T cells are separated by type using fluorescent-labeled antibodies to cell surface markers.
T cells are separated into helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, etc., by flow cytometry using antibodies labeled with different fluorophores (CD4-FITC, CD8-PE).
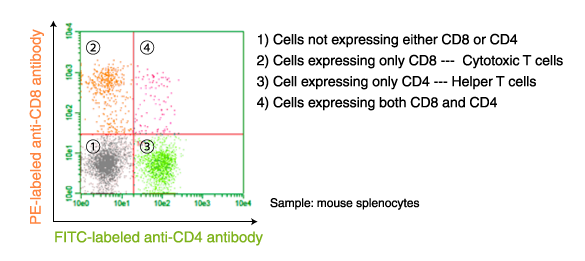
PE-labeled anti-CD8 antibody (Clone: KT15, Code No. D271-5)
FITC-labeled anti-CD4 antibody (Clone: GK1.5, Code No. D341-4)
Enzyme labelling
Enzyme-labeled antibodies are used for ELISA, Western blotting, and immunostaining. Labeled antibodies are detected by reaction with a substrate that emits light or changes color.
Commonly used enzyme
| Enzyme Name | Chromogenic Substrate | Chemiluminescence Substrate |
|---|---|---|
| HRP (Horserashis peroxidase) | DAB and TMB | Luminol-based (ECL) |
| AP | BCIP/NBT and pPNPP | Dioxetane-based (CDP-star®) |
Application example of enzyme-labeled antibodies: Immunohistochemical staining
The result of immunohistochemical staining indicates that autophagy was induced in the liver tissue.
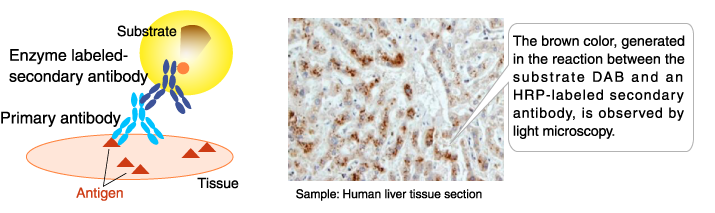
- Primary antibody: Anti-LC3 polyclonal antibody (Code No. PM036)
- Secondary antibody: Histostar™ (Rb) for Human tissue (Peroxisdase-labeled, Code No. 8466)
- Substrate: DAB Substrate Solution (Histostar™) (Code No. 8469)
Application example of enzyme-labeled antibodies: Western blotting
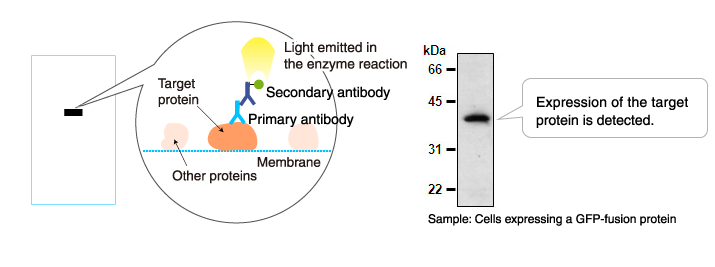
- Primary antibody: Mouse anti-GFP antibody (Clone: 1E4, Code No. M048-3)
- Secondary antibody: Anti-mouse IgG antibody (HRP-labeled, Code No. 330 (Only in Asia))
Biotin
Biotin-labeled antibodies are used in flow cytometry, immunofluorescence staining, and immunohistochemical staining. Biotin-labeled antibodies are detected by reaction with dye-, enzyme-, or fluorophore-labeled avidin.
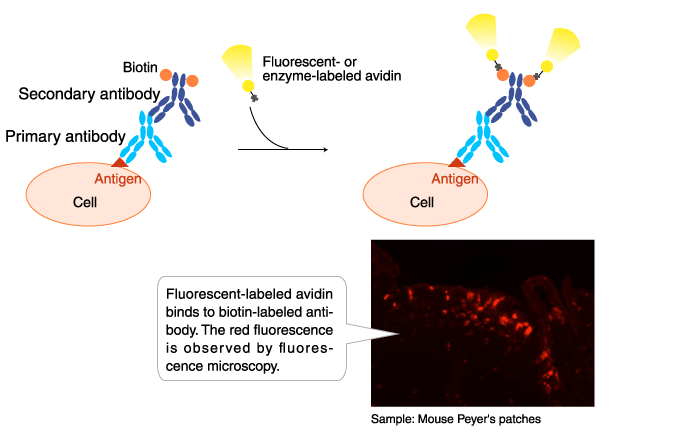
Antibody: Biotin-labeled anti-GP2 (Glycoprotein 2) antibody (Code No. D278-6)
Agarose, magnetic beads, magnetic agarose beads
Antibody-conjugated resins, such as magnetic beads and agarose, are used for immunoprecipitation.
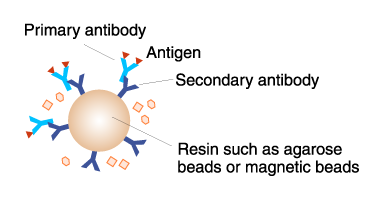
- The principle and method of immunoprecipitation (IP)
Colloidal gold
Gold-labeled antibodies are used in immunoelectron microscopy. This method is highly sensitive, and the signal does not fade as in fluorescent-labeling and enzyme-labeling.
Immunofluorescence staining with an antibody to an organelle marker.
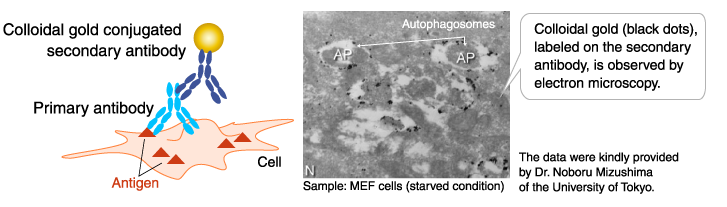
- Primary antibody: Anti-LC3 monoclonal antibody (Clone: 4E12, Code No. M152-3)
Related Links
Antibody
Antibody basics
Antibodies as a research tool
- How to generate antibodies
- How to select antibodies
- Labeled antibodies
- How to label antibodies
- Main causes of non-specific reactions
- How to reduce non-specific reactions
- Tags and Tag antibodies
Qualitative and quantitative measurements of proteins using antibodies
- Western blotting (WB)
- Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)