The Principle and Method of SDS-polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
In our introduction to SDS-PAGE we will explain the analytical technique to separate proteins based on their molecular weight.
When proteins are separated by electrophoresis through a gel matrix, smaller proteins migrate faster due to less resistance from the gel matrix. Other influences on the rate of migration through the gel matrix include the structure and charge of the proteins. In SDS-PAGE, the use of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, also known as sodium lauryl sulfate) and polyacrylamide gel largely eliminates the influence of the structure and charge, and proteins are separated solely based on polypeptide chain length. SDS is a detergent with a strong protein-denaturing effect and binds to the protein backbone at a constant molar ratio. In the presence of SDS and a reducing agent that cleaves disulfide bonds critical for proper folding, proteins unfold into linear chains with negative charge proportional to the polypeptide chain length.
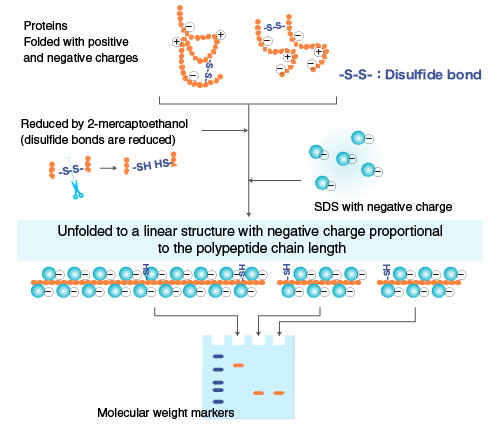
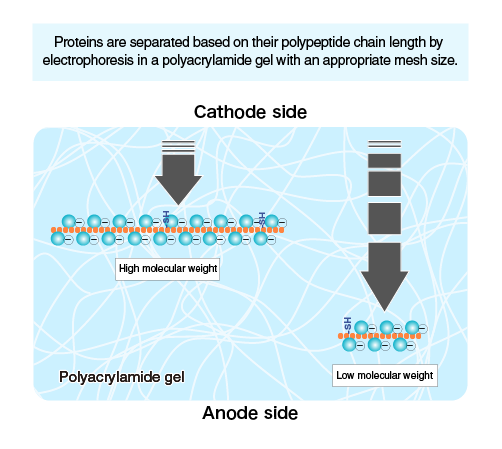
Polymerized acrylamide (polyacrylamide) forms a mesh-like matrix suitable for the separation of proteins of typical size. The strength of the gel allows easy handling. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of SDS-treated proteins allows researchers to separate proteins based on their length in an easy, inexpensive, and relatively accurate manner.
Procedure
Preparation of polyacrylamide gel
An example performed at MBL
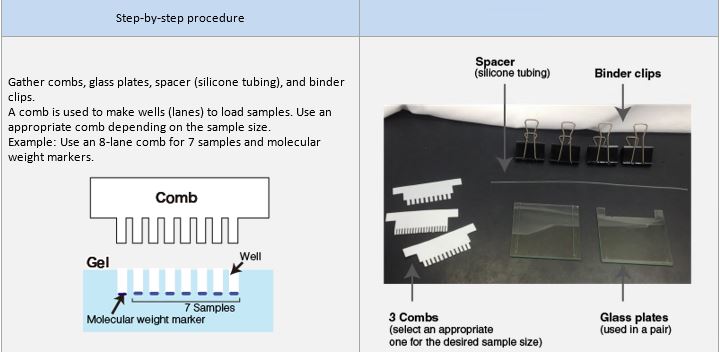


Preparation of samples
An example performed at MBL

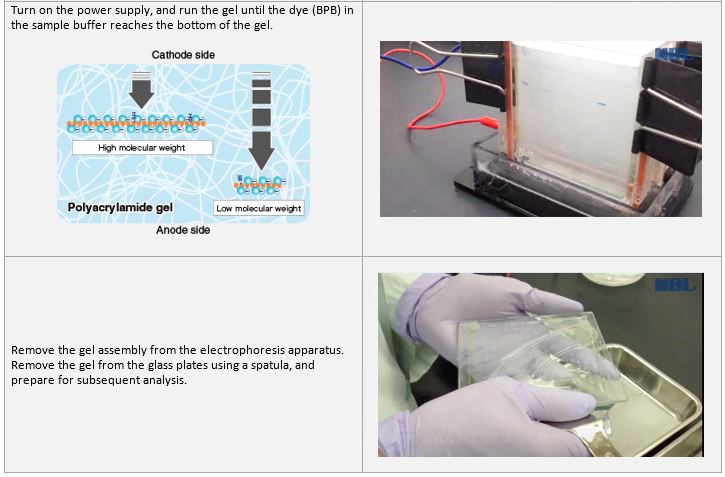
Electrophoresis
An example performed at MBL


Download our free Pathway Posters
Related Links
*Antibody
→Antibody basics
→Antibodies as a research tool
- How to select antibodies
- Labeled antibodies
- How to label antibodies
- Main causes of non-specific reactions
- How to reduce non-specific reactions
- Tags and Tag antibodies
*Qualitative and quantitative measurements of proteins using antibodies
- Western blotting (WB)
- Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)



