SARS-CoV-2 MHC-Peptide Screening Kit Bundles
Analyze antigen specific CD8+ T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 quickly and easily with the MHC class I QuickSwitch™ kits bundled with SARS-CoV-2 peptides. These bundles offer the possibility for researchers to create up to 8 different MHC tetramers within 1 day. Also, because 8 individual custom tetramers are not needed to be ordered, using this bundle provides significant cost savings. Most peptide sequences were selected from in silico screens of potential MHC binders (1) or from experimental studies (2) and were validated for high affinity binding to four different MHC class I alleles (3). In addition, this publication is also cited on Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) (4).
By performing peptide exchanges with the SARS-CoV-2 peptides of interest, researchers can use the new specificity tetramers for antigen specific CD8+ T cell staining, either individually or potentially as tetramer cocktails to advance research and understanding in this rapidly changing field. (Please note if using tetramer cocktails, staining assay optimization will be required by the end user.) The custom tetramer kit and peptides bundle provides a solution for quickly collecting useful data in a budget friendly and time friendly manner. MBL International supports all research to help understand the immune response to the SARS-CoV-2 disease. Contact us today with your specific questions in this important line of study.
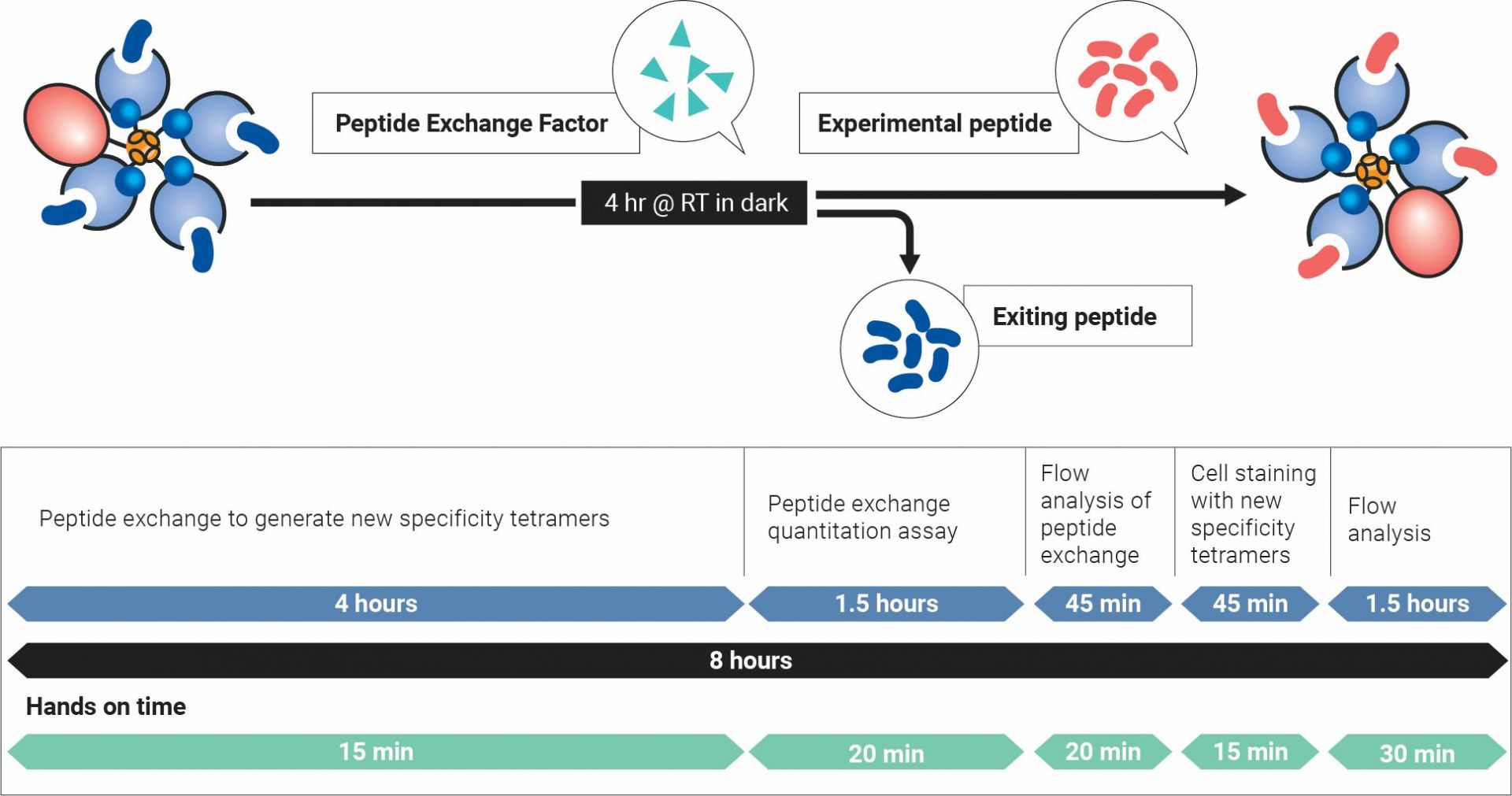
Overview of QuickSwitch™ Technology
HLA-A*02:01 QuickSwitch™ Kit and Peptide Bundles
| BUNDLE 1: PEPTIDES | PEPTIDE LOCATION | BUNDLE 2: PEPTIDES | PEPTIDE LOCATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLAHIQWMV | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (3122-3130) | YLYALVYFL | SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a protein (107-115) |
| FLLNKEMYL | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (3183-3191) | VVFLHVTYV | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (1060-1068) |
| LLLDDFVEII | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (6749-6758) | SIIAYTMSL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (691-699) |
| LLYDANYFL | SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a protein (139-147) | KLPDDFTGCV | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (424-433) |
| SMWALIISV | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (3732-3740) | ISDEFSSNV | ORF1ab polyprotein SARS-CoV-2 (5583-5591) |
| TLMNVLTLV | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (3710-3718) | RLNEVAKNL | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein |
| YLDAYNMMI | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (6419-6427) | YLQPRTFLL | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein |
| YLNTLTLAV | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (6851-6859) | RLQSLQTYV | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein |
H-2 Kb QuickSwitch™ Tetramer Kit and Peptide Bundles
| BUNDLE 1: PEPTIDES | TPEPTIDE LOCATION | BUNDLE 2: PEPTIDES | PEPTIDE LOCATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| VNFNFNGL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (539-546) | VVFLHVTYV | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (1060-1068) |
| MAYRFNGI | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (902-909) | SIIAYTMSL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (691-699) |
| INITRFQTL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (233-241) | VTQLYLGGM | ORF1ab polyprotein SARS-CoV-2 (5385-5393) |
| VVLSFELL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (511-518) | ITGLYPTL | ORF1ab polyprotein SARS-CoV-2 (5573-5580) |
| SIVRFPNI | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (325-332) | AAYYVGYL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (263-270) |
| GNYNYLYRL | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (447-455) | YNYLYRLF | Chain A, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (449-456) |
HLA-A*03:01 QuickSwitch™ Tetramer Kit and Peptides Bundle
| BUNDLE 1: PEPTIDES | PEPTIDE LOCATION |
|---|---|
| ASMPTTIAK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (2192-2200) |
| KSAGFPFNK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (4892-4900) |
| KTFPPTEPK | SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein (362-370) |
| STFNVPMEK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (2600-2608) |
| TTIKPVTYK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (1875-1883) |
HLA-A*11:01 QuickSwitch™ Tetramer Kit and Peptides Bundle
| BUNDLE 1: PEPTIDES | PEPTIDE LOCATION |
|---|---|
| ASMPTTIAK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (2192-2200) |
| KSAGFPFNK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (4892-4900) |
| KTFPPTEPK | SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein (362-370) |
| STFNVPMEK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (2600-2608) |
| TTIKPVTYK | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (1875-1883) |
HLA-A*24:02 QuickSwitch™ Tetramer Kit and Peptides Bundle
| BUNDLE 1: PEPTIDES | PEPTIDE LOCATION |
|---|---|
| DYVYNPFMI | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (6159-6167) |
| FYGGWHNML | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (4986-4994) |
| NYLKRRVVF | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab (3159-3167) |
Discover more about SARS-COV-2 REAGENTS
What is QUickSwitch™ Technology?
Related Content
QuickSwitch™ Starter Guide
MHC Tetramer Alleles List
Available MHC Alleles
Request our Tetramer Staining Guide
Request our new Tetramer Staining Guide
Immune Monitoring Webinar
References
- Candidate targets for immune responses to 2019-Novel Coronavirus (nCoV): sequence homology- and bioinformatic-based predictions Alba Grifoni, John Sidney, Yun Zhang, Richard H Scheuermann, Bjoern Peters, Alessandro Sette bioRxiv 2020.02.12.946087; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.12.946087
- The ORF8 Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Mediates Immune Evasion through Potently Downregulating MHC-I Yiwen Zhang, Junsong Zhang, Yingshi Chen, Baohong Luo, Yaochang Yuan, Feng Huang, Tao Yang, Fei Yu, Jun Liu, Bingfen Liu, Zheng Song, Jingliang Chen, Ting Pan, Xu Zhang, Yuzhuang Li, Rong Li, Wenjing Huang, Fei Xiao, Hui Zhang bioRxiv 2020.05.24.111823; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.24.111823
- Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 specific CD4(+) and CD8 (+) T cell responses using MHC class I and II tetramers. Poluektov Y, George M, Daftarian P, Delcommenne MC.Vaccine. 2021 Mar 5;39(15):2110-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.008. Online ahead of print.PMID: 33744048
- Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource