Pathway Posters
Pathway Posters
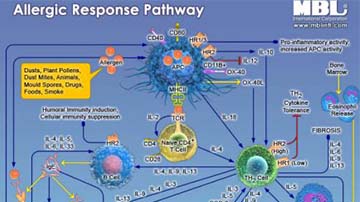
Pathway Poster: Allergic Response
PTPN6/SHP-1 plays a crucial role in negatively modulating insulin action and clearance in the liver, thereby regulating whole-body glucose homeostasis.
Pathway Posters
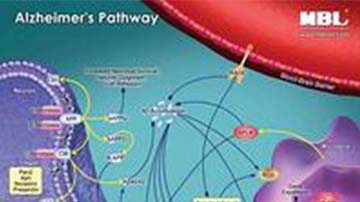
Pathway Poster: Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior. It is the most common neurodegenerative disease
Pathway Posters
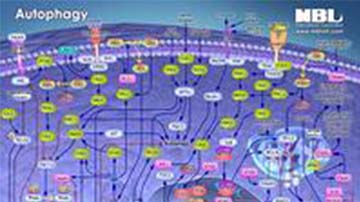
Pathway Poster: Autophagy
Autophagy is a cellular self-digestion process for the purpose of providing nutrients to allow for cell survival during stress conditions. Autophagy can be
Pathway Posters
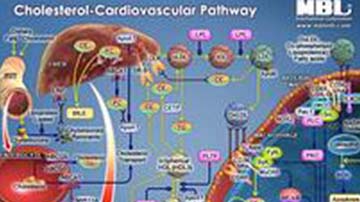
Pathway Poster: Cholesterol-Cardiovascular
MBLI provides reagents for quantifying PCSK9, which is secretory protein binding to receptor of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) to increase blood levels of
Pathway Posters
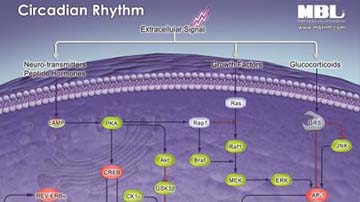
Pathway Poster: Circadian Rhythm
The circadian clock is a 24-hour endogenous oscillator, which cycles via transcriptional/translational feedback loops of clock genes
Pathway Posters
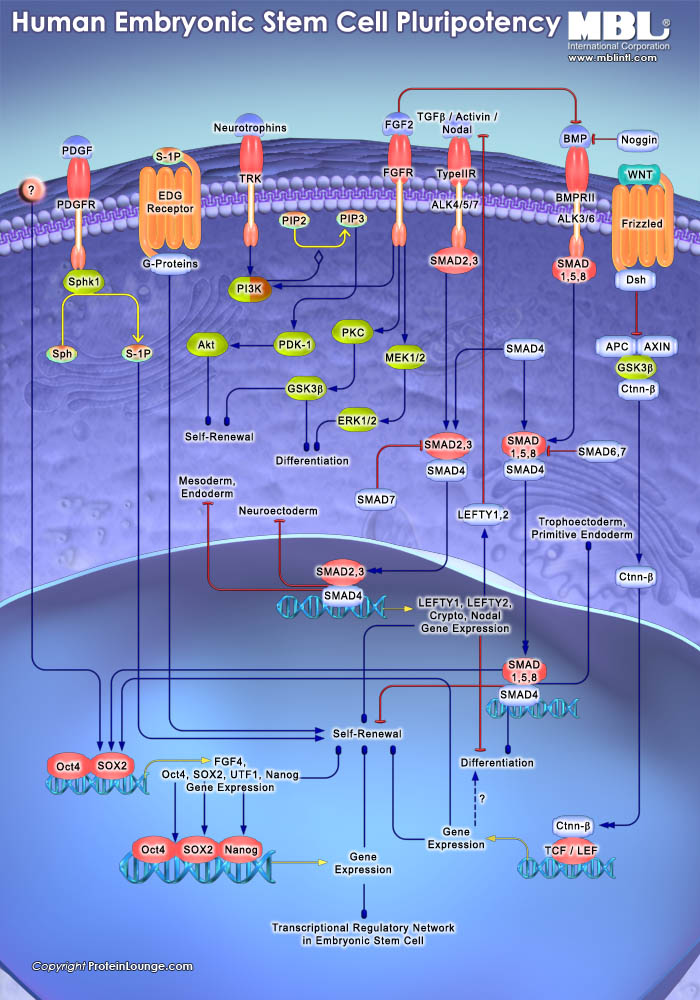
Pathway Poster: Human Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency
Recent studies with avian embryos and murine embryonic stem cells have suggested that hematopoietic cells are derived from hemangioblasts, the
Pathway Posters
Pathway Poster: Immuno-Oncology
The study of T-cell regulation is important due to their crucial role in the immune response. T-cells have special surface receptors that differentiate healthy and
Pathway Posters
Pathwway Poster: miRNA/mRNA
The main classes of small ncRNA are short interfering RNAs (siRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs) and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). siRNAs are generated
Pathway Posters
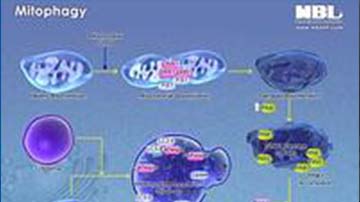
Pathway Poster: Mitophagy
Mitophagy detection vectors are designed for the co-expression of MT-mKeima-Red.
Pathway Posters
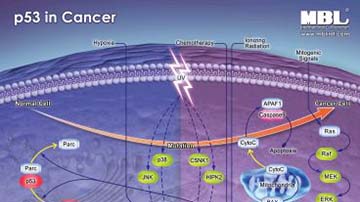
Pathway Poster: p53 in Cancer
p53 is an important factor in tumor suppression and is activated in response to cellular stress to induce cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. p53 mutants found in
Pathway Posters
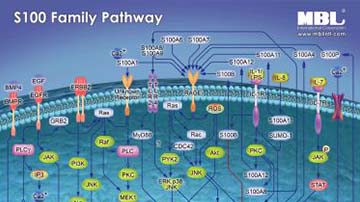
Pathway Poster: S100 Family
S100 protein family of calcium binding proteins with 2 distinct helix-loop-helix motifs (EF-hands) shows cell type-specific expression and consists of 20
Pathway Posters
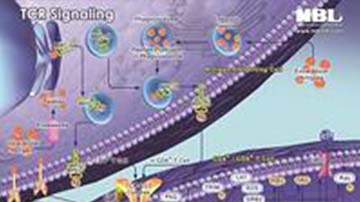
Pathway Poster: TCR Signaling
ZAP70 is a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase (part of the Syk/Zap70 family) that is involved in signaling by the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR). Ligation of the
Pathway Posters
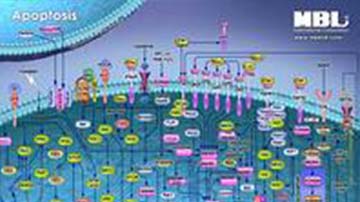
Pathway Poster: Apoptosis
Apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, is not only a major process within normal homeostasis but is present in disease states such as cancer and
Pathway Posters
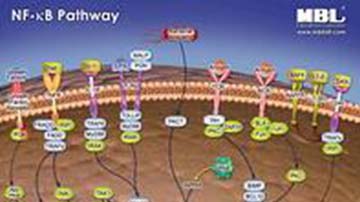
Pathway Poster: NF-KappaB
PTPN6/SHP-1 plays a crucial role in negatively modulating insulin action and clearance in the liver, thereby regulating whole-body glucose homeostasis.