CycLex® Cellular Histone Acetylation Assay Kit
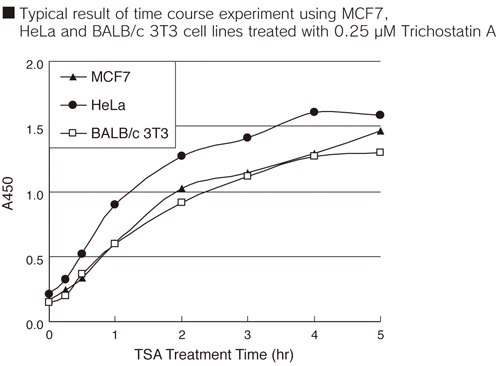
The CycLex Cellular Histone Acetylation Assay Kit is used for the semi-quantitative measurement of histone acetylation level in situ by means of cell-based ELISA It can be used for 2 x 96 wells.
| Target | Cellular Histone Acetylation |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Kit |
| Application | ELISA |
| Research Area | Cell Biology |
| Storage Temperature | 4°C |
| Protocols | ELISA |
| Regulatory Statement | For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. |